As we know,99 % of heat and 1% of the radiation is produced when any exposure is taken in for diagnostic or screening purposes. Here, nearly 90% of the radiation is not useful, so the left one must be utilized maximum, to get the optimum result. To execute this, the intensifying screens are introduced.
So, in this chapter of x ray course, we are going to learn about intensifying screens, how intensifying screens are made, types of Intensifying Screens, layers of intensifying screens, and much more.
Definition of Intensifying Screen
An intensifying screen is a thin sheet, that absorbs x ray radiation (photons), and converts them into visible light, is a part of the radiographic cassette, and acts as an amplifier for radiation.
Intensifying screens directly reduce the mAs during the exposure, reducing the radiation exposure for the patients and reducing radiation risks.

These are mounted on both sides of x ray cassettes in general radiography, while a single side is used in mammographic exams; mostly on the black side of the x-ray cassette.
Define Intensifying Screen in Dentistry
Dental radiographs are used for many diagnostic and treatment purposes of oral diseases, any abnormalities of teeth, or any oral pathology.
The radiation used here is very low and the ALARA principle is strictly followed.

Along with these, intensifying screens are also used in dental radiography, to minimize the radiation exposure to the patients. These intensifying screens in dentistry contain phosphor crystals for fluorescence effect when radiation is exposed.
Purpose of Intensifying Screens in Radiography
Intensifying screens are used to intensify the effects of the radiation, here; x ray photons.
Let’s discuss a few purposes of intensifying screens as follows:
- to provide a large number of light photons,
- to reduce the exposure duration,

These are two main purposes of intensifying screens in radiography.
Advantages of Intensifying Screen
Intensifying screens are very useful for improving final x ray image quality, and reducing the patient dose, These two are not enough yet, let’s discuss a few more advantages of intensifying screens as follows:

Lower Patient Radiation Dose
The main advantage of an intensifying screen is, that it reduces the patient radiation doses to a higher extent.
So, this saves the patient from unwanted radiation exposure and reduces the rate of radiation-related side effects or abnormalities.
Improves Image Quality
The second most important advantage of intensifying screens is to improve image quality. Along with this, it increases the film sensitivity by improving image contrast and details of the radiographic images.
These enhanced x ray images are easy to read and also help radiologists in better diagnosis.
Reduces Radiation Exposure Time
The third main advantage of intensifying screens is shorter radiation exposure time. The amplification effect of x ray photons on the x ray films boosts the x ray image formation by reducing the radiation exposure timing.
This decreases radiation exposure timing and again saves the patient from radiation exposure.
Cost Effective
The last but not least advantage of intensifying screens is cost-effectiveness.
With the help of intensifying screens, it reduces the consumption of x ray films and maintenance efforts.
These increase the lifespan of all x ray equipment, and their maintenance costs also.
So, here, these are the few advantages of intensifying screens like reducing radiation exposure, with image quality, and also making radiology imaging more effective and accurate for the radiology department.
Disadvantages of Intensifying Screen
Every coin has two faces, likewise intensifying screens also have their advantages and disadvantages. Here, we already studied a few advantages of intensifying screens and now we are going to learn the disadvantages of intensifying screens:

Loss of Image Resolution
The overall x ray image detail and image resolution are reduced because of the diffusion of light.
This also blurs the x ray images with a reduction of x ray image sharpness.
Screen Ageing
Due to regular uses of intensifying screens, the overall quality of this screen degrades or tears, due to use in repetition.
This intensifying screen aging leads to a weaker of its overall efficiency, resulting in improper quality of the x ray images.
Degradation of Phosphor Crystals
As we know, most intensifying screens contain phosphor crystals. The regular use of these crystals made them weaker and faded away over time. This leads to improper sensitivity, and light efficiency with decreased final x ray image quality.
Effects of Radiation Scattering
Sometimes, these screens cause radiation scattering and this leads to degradation of image contrast and also increases the background image noise.
To decrease the effect of radiation here, then we can use collimation or radiation shielding techniques.
So, these are the few disadvantages of intensifying screens including degradation of the material, or loss of image quality, etc. It’s very important to understand all these limitations.
Composition and Materials Used in Intensifying Screens
Spatial resolution is reduced but x ray film speed is increased. The thickness of an intensifying screen is about 0.4mm, and this will affect the speed of the screen and also spatial resolution.
So, here is a breakdown of all layers of intensifying screens are as follows:
Layers of Intensifying Screen
An intensifying screen contains many layers, designed to convert x rays into visible light. So, these are the components in a layer of an interesting screen:

Base layer
The first layer of intensifying screen is the x ray film.
The base layer is made of polyester and is 1 mm in size.
This layer provides mechanical support to the active phosphor layer.
Base layer must be moisture resistant, unaffected by radiation, and chemically inert and non-reactive.
Phosphor Layer
Also known as a luminescent layer.
It is the active layer of an intensifying screen.
It absorbs x-ray photos and converts them into visible light, and this layer contains a substance called ‘’Phosphers”.
Mostly, the thickness of this is about 50 to 300 μm, and the crystal thickness layer is about 5 to 15 μm.
This layer is crystalline and suspended in polymers, making it flexible.
The phosphor layer is mostly made up of rare earth metals like; (Gadolinium, Lanthanum, and Yttrium), and previously with Calcium Tungstate (CaWO4).
A few other types of types of material used in the phosphor layer are zinc sulfide and barium lead sulfate.
Reflecting Layer
The reflective layer is between the phosphor and the base layer.
The thickness of this layer is about 25 μm.
It is made up of magnesium or titanium oxide.
The reflective layer is made up of TiO2 and is 1 mm thick.
This layer redirects the radiation, if this is not available then most of the radiation directly reaches x ray film.
A Protective Layer
The protective layer is composed of a cellulose compound of 0.7-0.8 mm.
It is a very close layer to the x ray film also.
This layer prevents the intensifying screen from damage and is transparent to light, and also provides a cleaning surface area.
Many rare earth elements are used in today’s radiology, as these have high absorption and conversion rates;
Here are a few of them are:
Gadolinium: green light,
Lanthanum: blue light,
Yttrium
If the wavelength of light is initiated by the screen is not in the range of the native range, then this will be not absorbed and proceeded by the x ray film.
Here; the conventional films are sensitive to ultraviolet and blue lights, on the other hand, orthochromatic films are sensitive to ultraviolet, blue, and green lights
These are components of a layer of intensifying screen, and this combination optimizes the overall x ray absorption rates and image quality.
Explanation of How Intensifying Screens Works
The intensifying screen converts x-ray radiation into light, which passes through radiographic film and creates the latent image by reducing the amount of radiation.
In dentistry, this film is used for panoramic imaging and cephalometric radiography.
Let’s understand how intensifying screens works:
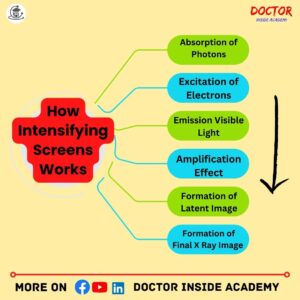
Absorption of Photons
When the radiation interacts with phosphor material in the layer of the intensifying screens, here, radiation is absorbed by atoms of the phosphor material.
Excitation of Electrons
Now, the absorbed radiation photos cause atomic movement in the phosphor atoms, where the energy level moves at a higher level, and this pose is also known as excitation.
Emission Visible Light
Here, light photons are released by the excited electrons. These light photons have their wavelength range in the visible spectrum.
Amplification Effect
These light photons now interact with silver halide crystals in the x-ray film, and this interaction goes with a chemical reaction and starts forming a latent image.
Formation of Latent Image
After the amplification effect in intensifying screens, there is a presence of latent image is seen.
Formation of Final X Ray Image
Now, this latent image interacts with photographic emulsion on the film surface, this process starts forming the final x ray image with attenuation of different body parts to show the different anatomical surfaces or body parts.
This overall process of how intensifying screens works makes the final enhanced x-ray image.
With better quality, and reduced radiation dose to the patient also.
Types of Intensifying Screens
These intensifying screens are classified based on the presence of components like phosphor, etc. So, here are a few types of intensifying screens:
Mostly screen uses rare earth elements like gadolinium, lanthanum, or yttrium.

Lead Screens
The lead screens are placed on both sides of x-ray film, so, these are also called as front and back screens.
Lead screens are made from lead foils, here the front screen also acts as a soft radiation absorber and absorbs the scattering of radiation also.
The lead screen intensifying screen is used mainly in x rays and gamma radiation.
The thickness of lead foils is 0.02 to 1.0 mm, depending on which radiation energy is used. Here; the front screen is about 0.02 to 0.20 mm and the back screen is usually of 0.25mm.
These lead screens are polished so that they are free from surface defects like scratches and will not be trained to the final x ray image after processing.
Lead screen intensifying screens are best suitable for radiation levels ar 80 keV to 420 keV, and not for high radiation energy.
These intensifying screens reduce radiation scattering and provide the best x ray image quality.
Also improves the image contrast and image, with decreasing exposure timing.
Steel and Copper Screens
In case of high radiation, lead is not best suited in these intensifying screens, here steel or copper screens are considered,
These are accounted for to get better image results in a high radiation energy range than lead screens.
Fluorescent Screens
Fluorescent screens work until exposure is continued, after the termination of radiation exposure, no fluorescence is seen.
These are made of a thin base layer, and that base layer contains crystallic metallic salt, usually made from calcium tungstate, which shows fluorescent characteristics.
This light sensitivity depends on the radiation density.
Flurometallic Screens
Flurometallic screens have properties that range between the lead screen and fluorescent screen and are made up of a lead-coated foil with a fluorescent layer.
These have shorter life spans than lead-intensifying screens.
These also provide appropriate image contrast in the radiographic image while considering reduced exposure time.
Here, the intensification of depends upon the sensitivity of the x ray film.
Last Words
So, today, we learned all about intensifying screens, how they work, and different types of intensifying screens with their advantages and disadvantages. We hope you enjoyed this chapter of our ”X Ray Course” by “Doctor Inside Academy”. If there is any doubt or query, feel free to contact our team in the Contact Us section here.
Checkout Our Latest Videos on Intensifying Screens
Disclaimer
The above chapter is designed, based on the author’s learning and experiences. so, this is for educational purposes only.
If you are using this chapter content, then you have to provide a proper citation or attribution to “Doctor Indide Academy”.
Any external links are used for references or citation purposes here, if any external status or information is changed, we are not responsible for any liability in that case.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are a few frequently asked questions regarding intensifying screens:
Why are intensifying screens used in radiography?
Intensifying screens are used to convert x ray images into light images, which enhances the x ray image contrast and overall x ray image quantity.
Why are intensifying screens added to an x-ray cassette?
Intensifying screens are added to x ray cassettes to enhance the image contrast, improve sensitivity, image brightness, and speed, and is very cost-effective.
How do intensifying screens reduce patient dose?
Intensifying screens reduce patient radiation dose by reducing radiation exposure because it intensifies the x rays and reduces its overall exposure time, to get a final x ray image with better quality.
What are intensifying screens used for?
Intensifying screens are basically used to get beer x ray images with reduced radiation dose, including better image sensitivity, and better contrast.
What is the purpose of the intensifying screen?
The main purposes of an intensifying screen are to improve the overall quality and efficiency x ray images in radiography, to get a better diagnosis, and to reduce radiation exposure to the patient.
How does intensifying screen affect contrast?
The image contrast is improved by intensifying screens and clarifies the difference between different body tissues to structures. This helps radiologists to diagnose or study images effectively and can pace between normal and abnormal tissues.
Intensifying screens in dental radiography
Intensifying screens are very important in dental radiography because by improving image quality and efficiency to get better dental radiographs, to diagnose oral abnormalities or any tooth abnormalities better.
What phosphor is used in intensifying the screen?
The most common phosphor used in intensifying screens is Zinc sulfide (ZnS) phosphor. This phosphor emits light when any amount of x rays is exposed towards it.
What material is used in intensifying screens?
The intensifying screen contains multiple layers, which are as follows:
- Emulsion layer,
- Phosphor layer,
- Protective layer,
- Outer layer
What are the factors affecting the intensifying screen?
Here are a few factors, affecting intensifying screens are:
Type of phosphor used,
Screen thickness,
Properties of emulsion layer,
Properties of Scintillator layer,
Environmental factors,
Image processing,
Detection systems,
Variation of the Tube Potential.
Variation of Tube Current.
Variation of Target-Film Distance.
Intensification Factors





