The main task of a radiographer is to select appropriate exposure values and safety measures to get optimum x-ray images concerning radiation exposure to the patient. These factors may include mAs, KvP, Grid, and trying to follow the ALARA principle, Source to mage receptor, etc.
To perform the x-ray image capturing task easily, go with the latest technology called automatic exposure control. Here, in today’s chapter, we are going to discuss automatic exposure control, its advantages, how Automatic Exposure Control works, types, advantages, and disadvantages, etc.
AEC is used in radiographic and mammographic imaging systems and provides better X-ray image output, with a reduction of radiation exposure to the patient.
What is Automatic Exposure Control
AEC is an x ray termination device.
AEC is known as Automatic Exposure Control, and these are the devices, that are used to control the amount of radiation exposure targeting the x-ray image receptors, here, these terminate the exposure automatically, when necessary.
To control the automatic X-ray exposure, a device is used named an Automatic Exposure Control Device, and sometimes also called a photo timer.

The main goal of AEC is to achieve the best quality images while minimizing unwanted radiation exposure.
Importance of Automatic Exposure Control
The importance of Automatic Exposure Control (AEC) is accounted for for many reasons, as it plays a very important in radiation protection and image quality.

A few Important factors of Automatic Exposure Control
These are –
Better Image Quality
AEC always ensures the quality of x-ray images, by terminating the exposure automatically, based on factors like patient size, tissue density, exposure value, etc.
It always takes care of image quality, with proper brightness and level of contrast, and helps in better diagnostic results.
Patient Safety through Dose Optimization
AEC helps to protect the patient from unwanted radiation exposure. It ensures only the needed amount of radiation will be accounted for and followed by termination of exposure.
Adaptive to Patient Variation
The patients vary in shape and size and the AEC calculates automatically these differences, for terminating the radiation exposure when needed.
Helping the Radiographers
AEC helps radiographers to choose the best exposure value, by automatically adjusting exposure parameters.
Radiographers must take care of patient positioning, and radiation safety of patients, and maintain a positive environment.
Prevention of Overexposure and Underexposure
AEC controls how much radiation is required to capture the desired x-ray image with better quality.
AEC prevents the image from overexposure or underexposure by the exposure value to prevent the patient from direct exposures and maintain x ray image quality.
Consistency Across Imaging Procedures
AEC ensures which part is going to be exposed and which type of examination is this. This keeps a standardized approach to maintain constant imaging results for different x ray images.
Reduces Repeat Examinations
The concept of testing the exposure automatically, when needed reduces the repetition of x-ray examinations because it already goes with the proper amount of radiation to ensure that the exposure gives better results.
This saves patients from double radiation exposures and saves costs for hospitals or diagnostic centers, along with their time and resources.
Integration with Digital Radiography
AEC is simply embedded with digital radiography systems, which enhances the imaging results and becomes a time-saving process.
Image post-processing is also enhanced by the integration of AEC in the system.
Enhanced Patient Experience
The overall patient experience after the integration of AEC in radiology is impressive, as this saves time and gives better images.
This increases the chances of positive feedback among the patients.
So, these are the few important of AEC to maintain patient care by ensuring patient safety and receiving better quality images.
Types of Automatic Exposure Control
Automatic Exposure Control controls the amount of radiation reaching the x ray image receptors and terminates the exposure when needed.

There are different types of AEC systems; classified based on the devices used to convert the radiation into signals; (electricity).
- Phototimers AEC System
- Ionization Chambers AEC System
- Solid State AEC
- Dual Field AEC
- Pulse Fluoroscopy AEC
- Automatic Filter Selection AEC
Let’s understand these all in detail;
- Phototimers AEC System
Phototimers contain photodiodes as light-sensitive detectors, that convert light energy into electrical energy.
Photodiodes sense the intensity of transmitted radiation and terminate the exposure when proper radiation is received.
Phototimers were used in 1st generation of AEC systems.

Phototimers are not used in today’s medical imaging, because ionization chamber systems replace these.
These are placed after the x-ray imager receptors, and the timers are also embedded with them so that they terminate the exposure when needed, known as exit-type devices.
Phototimer systems in AEC are used commonly in general radiography and fluoroscopy.
- Ionization Chambers AEC System
Ionization chambers are ion chambers or gas-filled chambers, with a hollow shape inside and contain the air with a timer and electric wire.
These are known as entrance-type devices because they are placed in front of x-ray image receptors and after the patient.
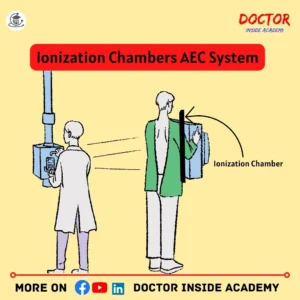
When an exposure is processed, the air measures the radiation that passes to the patient, and an electric charge is created, that travels through the wire used, to the timer and exposure is terminated automatically, when needed.
In modern times, AEC controls ionization chamber systems, because there are very few failure factors.
Ionization chamber systems are used in general radiography, fluoroscopy, or with higher dose systems.
Solid State AEC
Solid-state AEC contains amorphous silicon or selenium and converts the radiation into electrical signals.
When the exposure is made, amorphous silicon calculates the amount of radiation and terminates the exposure, when needed.
These are very efficient in capturing x ray images and evaluating the proper radiation exposure with the best signal-to-noise ratio (SNR).
Solid-state AEC is used most commonly in digital radiography.
Dual Field AEC
Dual field AEC contains ionization chambers and solid state detectors and is placed at different locations in the x ray image receptors.
This dual-field configuration, helps the systems to calculate the specific areas and is mostly used when body parts with different densities are captured in a single x-ray image.
Mostly used in chest X-rays, where lungs with mediastinum have different density levels.
Pulse Fluoroscopy AEC
Pulse fluoroscopy AEC is used most commonly in fluoroscopy, as there is continuous exposure to visualize the internal organs in real-time.
When continuous exposure is initiated, this AEC detects and maintains the adjustments of radiation exposure and then terminates the exposure to capture better-quality x ray images.

The most common uses of pulse fluoroscopy AEC in cardiac catheterization, barium studies, or interventional radiography are to view real-time actions.
Automatic Filter Selection AEC
The automatic filter selection system in AEC selects the x ay beam filters based on the shape or size of the patients.
These choose the filters accordingly, to optimize the image output and radiation exposure to that body and always take care of x-ray image contrast.

Most commonly used in Mammography exams to enhance the breast tissues or abnormalities for better diagnosis.
These are the different types of Automatic Exposure Control, based on their types, demand, or uses in the diagnostic centers our hubs, and all AEC systems to improve the x-ray image and reduce the unwanted radiation exposure to the patient.
Milliampere/Second Readout in AEC
Milliampere/Second Readout is a display factor; showing how much radiation is needed to capture the x-ray image.
It simply measures the rate of electrical charge flow through the photoelectric sensor due to the radiation exposure and is used to capture the final x-ray image while terminating the exposure.
As it is the by-product of tube current(mA) and the exposure time(s).

Milliampere/Second Readout displays the reading, after exposure termination.
This helps the radiographers to understand the amount of radiation needed and makes it easy for upcoming exposures.
This monitors the exposures, feedback of exposure control, dose optimization, and termination criteria, with quality assurance.
So, Milliamperage/Second Readout is very important in Automatic Exposure Control, as it evaluates a few technical concerns to get the final x-ray image output.
MaS, KvP Selection in AEC
MaS and Kvp are the essential factors for every exposure. These reflect the image clarity, contrast, brightness, etc, that directly help in diagnosis.
KvP must be used properly if AEC is entitled.
If higher the KvP is higher, exposure becomes shorter and AEC decreases the exposure; here, radiation exposure to the patient is reduced.
Components of AEC Systems
Automatic Exposure Control is made up of many components, like detectors, timers, wires, etc.

Here are the components of AC systems:
- Types of Detectors
There are many types of detectors used in AEC systems, based on their usages or workload, like ionization chamber detectors, solid state detectors, automatic filter selection AEC, etc.
- Control Panel and Settings
The control panel has a visual display, that shows the value at which AEC works and can be adjusted according to the thyme of shape or size and tissue density or thickness of the patients.
- Integration with X-ray Equipment
AEC is known as exit-type AEC systems or Entrance-type AEC systems, based on their placement with the x ray image receptors.
If AEC is placed after the x ray image receptors, then known as exit type, and if in the front, then known as entrance type AEC systems.
So, these are the main components of AEC systems to work effectively.
How AEC Works
Automatic Exposure Control is an exposure termination device, that is used during exposure to monitor the radiation exposure and maintain x ay image quality.
Now we are going to discuss the automatic exposure principle and a step-by-step breakdown of how AEC works.

Working Principle of Automatic Exposure Control
Automatic Exposure Control works on a feedback mechanism loop, where radiation is targeted on the patient and converted into an electrical signal, here, AEC calculates the amount of radiation when the appropriate level is reached, it terminates the exposure and saves the patient from unwanted exposure and ensures the final x-ray image with better quality.
Along with this principle, AEC works differently based on MAs, KvP, and which type of filter is used in that system.
Explanation of How Automatic Exposure Control Works in X Rays
Here is the step-by-step process of how the automatic exposure control works in x rays in radiology –
- Patient Positioning
The radiographer must take care of which body part is going to be examined, proper alignment, and proper x ray beam focusing must be entitled to get the best diagnostic result.
- Placement of AEC Sensor
After positioning, we must be aware of which type of AEC sensor is working in the system, that may be an entrance type device or exit type device.
As these AECs are very sensitive to radiation.
- Selection of Protocol
The radiographer must select which type of x ray exam is going to be performed, with proper exposure setup in the exposure panel in x ray system.
The software has pre-installed protocols for every diagnostic exam like chest x ray, abdomen x rays, or upper or lower extremities.
- Exposure Initiated
Now, it’s time to initiate the exposure, here the x-ray tube emits radiation and targets the patient, already focused and aligned.
- Radiation Exposure Monitoring
Now, AEC sensors monitor the continuous radiation transmission, with their intensity. These sensors are very sensitive to detect radiation and this monitoring is in real-time.

- Feedback Loop Mechanism
As we already discussed, it works in a loop system, where the amount of radiation with its intensity is monitored and maintains the desired radiation exposure to get a better diagnostic x-ray image.
This loop maintains the x ray image quality and takes care of overexposure or underexposure.
- Termination of Exposure
AEC checks the level of radiation and then terminates the radiation exposure when the proper level of radiation is reached. This ensures better image quality and prevents patients from unwanted radiation exposure.
- Image Quality
Now, we get the best x-ray image quality, based on the types or size of the patients varying in their tissue densities or anatomical ranges.
This is how Automatic Exposure Control works and how it adjusts the radiation exposure, dose optimization, and reduces exposure repetition, and better image quality.
Advantages of AEC
AEC is very beneficial for getting consistent X-ray images, as sometimes it is very difficult to handle patients varying in shape or size but AEC wins this situation because it takes care of the quantity of radiation and quality of the image.

Here are a few advantages of AEC in X Rays are –
- Better Image Quality
AEC terminates the exposure, when necessary, and it maintains the x ray image quality with better visual results and consistency.
It automatically detects the size of the patient with their tissue densities and gives an accurate diagnosis.
- Dose Optimization
AEC takes care of how much amount of radiation is given to the patient and as we k wo that this terminates the exposure when an adequate level is reached. So, it optimizes the radiation dose according to the patient and study performed
This saves patients from unwanted radiation exposure and gives better x ray image quality.
- Patient Variations
Patient varies in shape or size based on their gender and age with their tissue densities.
AEC detected automatically these differences and works accordingly to keep the optimized outputs.
- Reduce Workload for Radiographer
AEC increases the efficiency of the radiographers, by the selection of exposure accordingly and termination, and radiographers can focus more on patients [psotiuon, patient safety, or keeping a positive environment for the patient during the diagnosis.
- Overexposure or Unexpsoure
AEC helps to maintain regular radiographic densities in the x ray image.
AEC systems prevent final x-ray image output from underexposure or overexposure because they select the optimum level of radiation, keep the timer on, and dismiss the exposure when required.
Overexposure to radiation causes harm to patients and underexposure leads to poor image quality. If AEC is integrated, these both will be solved easily.
- Avoid Repetition Examinations
AEC helps radiographers avoid the x-ray exams being scheduled again and again for the same patient due to overexposure or underexposure because it takes control of that and reduces the repetition of x-ray exams.
This saves time, effort, and patients from additional radiation exposure and costs to the department and its resources.
- Used in Many Applications
AEC is very adaptable and is used in general radiography, digital radiography, fluoroscopy, mammography, and computed tomography.
These are the few advantages of AEC including optimization of radiation, along with taking care of final x ray image quality, following the ALARA principle that ensures patient safety and diagnosis efficiency.
Disadvantages of AEC
As we learn about a few advantages of AEC, along with these AEC has a few disadvantages also, that become challenges for the department or radiographers sometimes.

These are the following –
- Improper Selection
Sometimes, radiographers select different exposure factors, which will lead to unwanted radiation to the patient and repeated exposure with consumption of resources and time or effort.
- Positioning Error
Sometimes, a different anatomical position is selected then AEC misinterprets the examination and will not achieve the required exposure parameters, leading to x ray image artefacts or repateing of the exposure.
- Implantation Error
Any type of implantation in the body, like dental implants, hip or shoulder implantation; causes the overexpose of X-ray image receptors via ionization chambers, because this metal absorbs the x-ray beam or competes with that x-ray beam.
AEC faces difficulty in managing the exposure which again leads to x ray image artifacts.
- Equipment Cost and Maintenance
Integration of AEC costs more than the normal systems, as needs regular calibration, and regular maintenance.
- Become Unsuitable for Few Modalities
AEC is used to result in general radiography, flurosc[oy, and mammography. Sometimes, these integrations do not compete with the systems, then their alternate exposure control devices will be considered.
- Proper Training
Radiographers must be aware of the benefits and working of the AEC perfectly, otherwise, this will lead to improper selection of exposure leads to poor x ray image quality.
These are the few disadvantages of AEC and radiographers must be aware of these all and take care of them. These all need proper training, regular maintenance, and best practices to keep the AEC working efficiently.
Factors Affecting AEC
It’s very important to optimize the AEC and their parameters to get better results with dose optimization.
Many factors directly affect the performance and working of the AEC.

Here the key facritd afectign AEC are:
Patient Positioning
Patient positioning is very important while performing any type of x ray exam, then this helps AEC to perform accurately.
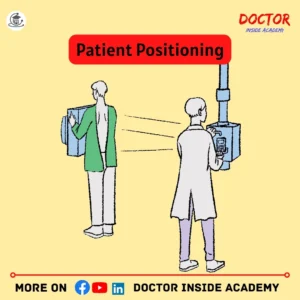
Improper positioning with variations like tissue density, and thickness, leads to poor images or wrong diagnostic x ray images will lead to improper diagnosis also.
Patient Anatomy
The anatomical difference sometimes leads to improper functioning of AEC. So, before initiating the exposure, the radiographer must ensure which body part is going to be examined.
Patient Size
Patient size varies based on their age or gender. So radiographers must take care of exposure value before performing the exams, to get the optimum result with proper utilization of AEC functioning.
Body Tissue Densities
The major density difference is seen between fats and muscle tissues and these both accounted in the attenuation of x-rays.
So, AEC must be adjusted to maintain the x ray image quality and radiation exposure.
Metal Implants
Body piercing or metal implants affect the AEC’s functioning and working, and it becomes complex for the AEC to perform well.
These implant metals cause more x ray attenuation, which will lead to x ray image artifacts sometimes.
Collimation or Field Size
The degree of collimation or how much field is open for radiation intake must be considered. This affects the radiation to reach the AEC, and this will lead to image artifacts or improper AEC functioning.
Grid Selection
X ray Grids influence radiation exposure and will affect the AEC working. So, proper attenuation of x rays must be considered while using grids to get better performance.
Source to Image Distance (SID)
The distance between x ray image to the sources influences the amount of radiation used and intensity is also considered. So, AEC systems must be adjusted accordingly based on the SID to maintain the final x ray image quality.
A few other factors must be Considered
If Ma is increased, it decreases the exposure timing,
Same with KvP, as KvP increases, it decreases the timing of duration,
If the distance between the source and the detector is increased, thus will increases the exposure timing,
If collimation decreases, then it increases the exposure time,
If collimation is fully open, this will lead to radiation scattering,
So, radiographers must be aware of these factors to get a better final x ray image.
Proper equipment installation and maintenance must be considered to maintain the functioning and working of the AEC.
Applications of AEC
AEC technology is a very flexible one, as it is used widely in many diagnostic modalities.
These are used to optimize the radiation dose with consistent image quality.

Here are a few applications for AEC in Radiology:
AEC in General Radiography
AEC is commonly used in general radiography in various diagnostic examinations such as chest x rays, abdominal x rays, lower or upper extremities or to examine bony structures.
In plain radiography, AEC uses just one or two thin radiation ionizing chamber which is placed between the patient and the X-ray receptor, and keep track of patient size and tissue densities to deliver the best x ray image output.
AEC in Mammography
Mammography uses very low radiation dose, so AEC is kept behind the x ray image receptor to avoid shadow casting.
Dose optimization must be accounted for during mammographic exams, so proper exposure setting must be entitled.
AEC in Fluoroscopy
Pulse fluoroscopy AEC system sussed in fluoroscopic diagnosis, as here real-time imaging is performed to view the live internal organs or tissues to evaluate different types of abnormalities.
The most common uses of AEC in fluoroscopy are barium studies, cardiac catheterization, or interventional imaging.
AEC in Computed Tomography
AEC in CT determines the shape and size via sonogram or scout view and then the tube current is adjusted,
Rotational modulation is induced here, as few systems detect output in every rotation with previous attenuated data.
AEC in Mobile Radiography
Portable or mobile radiography systems are used to capture x ray images by bedside.
These also have equipment with these AECs that are used to get better x ray images and radiation optimization without any manual adjustments.
AEC in Chest Radiography
The chest region has a different tissue density range, with chest wall thickness varying from patient to patient. So, AEC is used during chest radiography to maintain the quality of the diagnostic result.
AEC in Orthopedic Imaging
AEC used in orthopedic imaging ensures the variation of bone densities and tissue thickness and gives the desired results.
AEC in Pediatric Imaging
AEC is very important during Pediatric imaging, as there very little radiation exposure is needed.
Here, AEC is accounted for the role of capturing the best diagnostic images with minimized radiation exposure to that baby or infant.
These are the few applications of AEC, used in various radiographic modalities to ensure the quality of the image with patient dose optimization.
Comparison of AEC with Manual Exposure Control
The selection of radiation exposure for any x ray exams is very important. The exposure is the product of MAs and KvP, so these must be entertained properly to get optimum results.
AEC is used to produce better-optimized x-ray images, so AEC plays a very crucial role in the radiology department, as these devices help radiographers to determine what amount of radiation is considered to produce high-quality x-ray images.
Before introducing AEC in radiology, Manual exposure selection is performed, to get the final x ray image. These factors are KvP, MAs, SID, image receptors or grid, etc to determine the final exposure value.
The introduction of AEC in radiology saves a lot of time, effort, and resources to get the desired x-ray image and proper dose optimization, because manual exposure selection is a little bit difficult, based on the different types of patient shapes or sizes, tissue density or thickness and much more must be considered.
These all were not best accounted for during the manual exposure, but AEC detects all factors automatically and, presents the reflected value to get better results.
Last Words
Today, in this chapter, we learned all about AEC, its types with benefits, and its limitations and comparison with manual exposure. As AEC is a very important part of the radiology department every radiographer must be aware of that, how it works, and its advantages and disadvantages.
Disclaimer
The above information is based on the learning, research, and experience of the author, and this chapter is for educational purposes only.
If any external source is mentioned, then we are not responsible for the same, if any change or removed from the web.
If you are using this chapter’s content as yours, then you need to give credit to the author and write accordingly, not the same as above.





Pingback: Understanding Radiographic Exposure Factors - Doctor Inside Academy