After taking admission to any course, we need to study its subject matter and do projects, do internships in that zone and after 3 to 4 years, we will be awarded the desired degree by our recognized university.
Here, I passed out from medical imaging technology and faced many problems in my paramedical career. So, I started Doctor Inside Academy, which is a solution for paramedical students and makes every subject easy to understand in a friendly way.
Free X Ray Course For All Radiology Students
This free course is specially designed for bachelor’s and master’s students who are pursuing a degree or diploma in radiology.
In this series, we learn about the introduction and properties x rays, the history and production of X-rays, principles of radiology, x-ray imaging techniques, imaging evaluation, quality control, quality assurance, patient care and safety in radiography, legal and ethical considerations, and future trends in radiography.
So, this is chapter 1 of an x ray course for paramedical students.
What is Radiation?
Radiation plays a very important role in the radiology field and helps healthcare professionals to obtain diagnostic images where physicians can detect, diagnose, and treat various medical abnormalities and conditions.
Radiation Definition – Radiation is an energy, which flows in waves and particles and has electric and magnetic fields simultaneously, hence called electromagnetic waves.

Radiation has many advantages in our day-to-day life, and this comes from natural or man-made sources. Radiation can be absorbed, and scattered by any objects or bodies, on which it was directed.
The sun is a natural radiation emitter and mostly natural radiation cannot harm an individual’s health. Radiation can ionize the atoms, by knocking out electrons from their shells, and this ionization can cause harm to biological tissues.
Types of Radiation
Few radiations are harmful and the rest are harmless, based on this, Radiation is further divided into two categories, are followings;
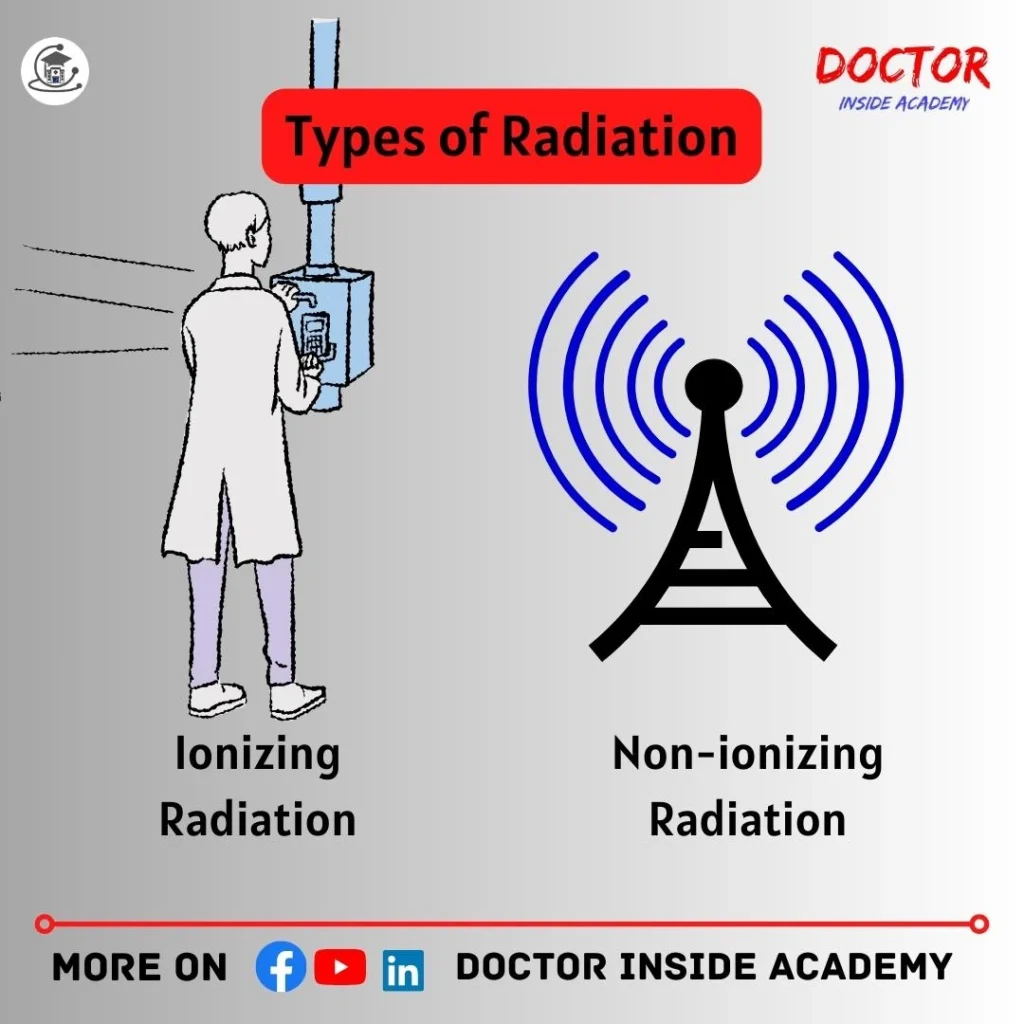
Ionizing Radiation
Ionizing radiation has enough energy that can produce ions in matter and can remove electrons and make it ionized.
Ionizing radiation has a shorter wavelength and higher frequencies If this ionization takes place in the human body, then it will harm the target biological cells and also affects adjacent one and can damage DNA, causes skin burns, or risk of cancer,
This, ionizing radiation includes the following based on their interaction levels are;
- alpha particles,
- beta particles,
- gamma rays,
- x-rays
Non-ionizing Radiation
Non-ionizing radiation has not enough energy to ionize the atoms and is unable to cause ionization.
This only produces heat and may cause little skin burns, if exposed long.
This, non-ionizing radiation is also divided into further categories are followings, based on their energy levels are;
- Radio waves,
- Microwaves,
- Infrared waves,
- Ultraviolet rays,
- Visible light,
What is X Rays?
X-rays are the oldest form of radiation used in medical imaging for diagnosis and treatment purposes.
X-rays are a form of electromagnetic energy, where it possesses electric and magnetic properties.
X-rays were accidentally discovered by William Concard Roentgen in 1895.
X-rays are produced by passing an electric current through a vacuum tube containing two electrodes anode and cathode.
When these X-rays are passed through the human body, they may be absorbed, scattered, or reflected by the medium, depending on their densities and interactions.
Calcium blocks X-rays and appears white on the X-ray images and the black region that appears on the images shows air and a few gray shades show fluid, blood, or soft tissues.
What are X Rays Uses?
X-rays are used for screening, diagnostic, and treatment purposes to a greater extent.
X-rays are used to evaluate the followings;
- Broken Bones,
- Dislocated Joints,
- Disorders,
- Diseases,
- Infections,
- Tooth Decay,
- Arthritis,
- Breast Tumors,
- Any Swallowed Items,
- Digestive Problems,
- Enlarged Heart, etc.
X-rays are detected by X-ray cassettes, then converted into hard copies through printers and software.
X-rays are used in different modalities like X-ray machines, ct, fluoroscopy, mammography, etc.
X-rays are avoided during pregnancy because this will lead to birth defects or other severe abnormalities in their offspring.
Properties of X Rays
The x-rays have their properties and values, which are given below.

- They are the form of electromagnetic radiation,
- They are invisible,
- They carry enough energy to ionize the atoms,
- They are harmful to the biological tissues,
- X Rays have high penetrating power,
- They have a shorter wavelength ( 0.01 to 10 nanometers ) and higher frequency,
- It travels at the speed of light in a vacuum,( 3*10 power*8ms ),
- X-rays have no mass,
- X-rays travel in a vacuum and also in a straight line,
- They cannot be affected by magnetic and electric fields,
- X-rays produce images on photographic films,
- These require high voltage current to produce x-rays in the x-ray tube,
Different Types of X-ray Studies
X-rays are used for diagnostics and treatments for different abnormalities and are a painless procedure that saves the life of patients at the very early stages of any disease.
Few Common x ray study are following’s;
Body Parts X Rays
- Upper or lower extremities, spine x-rays, neck, pelvis, skull, joints, etc,
Bone X Rays
- Fractures, dislocations, arthritis, bone cancers,
Chest X Rays
- X-rays of the chest, lungs, heart, ribs, diaphragms,
- abnormalities of the heart, lungs, bones in the chest, cough, pneumonia, tuberculosis, lung cancer, ribs fractures, etc,
Abdomen X Rays
- Used to study the organs and structures in the abdomen such as intestines, stomach, spleen, kidney, stomach, liver, bladder, etc,
- Used to diagnose conditions like Kidney stones, bladder stones, barium enema, blockage, injuries to internal organs, etc,
- X Ray Contrast studies are also taken.
KUB X Rays
- Especially for urinary conditions, GI Tract problems,
- Evaluate the shape, size, and position of your kidneys, ureter, bladder,
- Mostly done for kidney or ureteral stones,
Dental X Rays
- Imaging of teeth and mouth,
- Diagnose infections or check cavities,
- OPG; the most common,
Mammography
- X-rays of the female breast,
- Used to diagnose breast lumps, nodes, breast cancer,
- Used for screening or diagnostic purposes,
Computed Tomography
- Uses x-rays to create cross-sectional images of body organs, tissues, bones, etc,
- It gives better visualization than routine radiographic images.
Fluoroscopy
- Produces moving images of the different organs.
X ray Contrast Studies
These are the studies, which are followed by the administration of contrast media in radiology,
X Ray contrast media highlights the specific area on the body with more details.
Different forms of contrast media in radiology are powder gases, suspension, and liquid and administered to the body by different routes are oral, rectal, or IV,
It’s a risk vs benefit procedure.
Different X Ray Contrast Study Procedures;
Esophagram
- Exam of pharynx and esophagus use of still or fluoro images,
- Images are taken after the patient drinks a solution that coats the walls outlines of the esophagus ( Barium Swallow);
Upper GI Series
- Series of x rays of the esophagus, stomach, small intestine,
- Contrast is drunk by the patients,
- Used to identify ulcers, tumors, inflammations, etc,
Small Bowel Series
- X-ray series extended to the large intestine,
Barium Enema
- X-ray series of colon and rectum,
- Used to identify diverticulitis, dilation of the colon, polyps, cancer, obstruction, fistulas, etc,
Angiography
- X-rays of blood vessels,
- Used to check the functions of blood vessels in the heart, lungs, kidneys, brain, arms, or legs,
- Diagnose conditions like tumors, obstruction, nodes, etc,
HSG
- Used to evaluate fallopian tubes, the uterus is normal,
- X Ray contrast media is injected into the cervix,
Arthrogram
- Contrast study of joints,
- Used to evaluate abnormalities of joints, legs, or arms,
IVP
- Contrast study of kidney, ureters, bladder,
- To diagnose kidney stones, enlarged prostate, tumors in KUB, cysts, surgery, or any other abnormalities,
RGU/MCU
- Contrast study of male urethra region,
Precautions taken during the use of X Ray Contrast Medium are given;
- Proper instructions must be followed,
- Fasting,
- No metal or jewelry on the body while performing the scans,
- Asked to empty the bladder,
- Holds the breaths,
- Remains still during the procedures,
- Allergic patients must report before the studies,
- Pregnancy, diabetics, COPD, Asthma, etc are reported immediately,
Risks of X Ray Contrast medium
- Reactions may be mild, moderate, or severe,
- Hives, itchiness, shortness of breath, weakness,
- Patients with kidney problems are at higher risk,
- Vomiting, cramps, constipation, possible side effects,
- Diabetic patients are most prone to risk, which may lead to kidney abnormalities,
Applications of X Rays

- Used in Radiotherapy;
- to kill diseased cells and malignant tumors,
- This also harms the healthy cells and tissues,
- Used in Medical Sciences,
- fractures, infections, diagnosis and treatment of different types of diseases,
- Used in Security,
- luggage of passengers at airports, and rail terminals,
- Used in Engineering;
- to investigate the structures of metals, and gas pockets,
- detect cracks,
- get insights into internal structures,
- Used in Research and Development
- are usd to study structures and properties of elements,
- To study the composition of crystals,
- The behavior of molecules or compounds,
How X Ray Radiation Affects the Human Body?
The x ray side effects cause the ionization of atoms which affects the molecules of the human body and further affects the cells, tissues, organs, and the whole body.

Radiation has different effects depending upon the area exposed.
Following are the effect of x ray on human body:
- Hair, brain, thyroid, blood, reproductive organs, skin, bone marrow, eyes,
- Radiation can damage DNA,
- Causes cancers, but very rare yet,
How were X Rays Named?
At the time of discovery, the nature of these X-rays was unknown, and Roentgen was good at mathematics. We use unknown values such as X while solving any mathematical calculations, and Rontgen was also confused about the name of this new type of radiation and he finally named them X that represents unknown. Hence, x-rays are unknown rays.
The name was from his name Rontgen also, called Roentgen Rays.
How X Rays Work?
Lets learn how x ray working?
X-rays have a shorter wavelength and high penetrating power, and are produced by X-ray tube, and then directed to the human body to take radiographs for diagnostic or screening purposes.

These X-rays are absorbed by different tissues in our body that have different densities, so, the radiographic densities create different shades on the X-ray film, based on their tissue types, and x-ray absorption.
Here, bones contain calcium, and particles are tightly closed enough that don’t allows x rays to pass through them, and have a higher atomic number and absorb the x rays and the image becomes white hence, bones appear white on the X-ray film,
On the other hand, x rays travel in low-density areas easily and appear black in the X-ray film, i.e- air, fluid, fat, etc,
These different densities are shown on the final X-ray images that help in diagnosing and treatment of different diseases or abnormalities of the patients.
Last Words
In this chapter 1 of X Ray Course, we learned about x ray radiation and its types and all about x-rays and their properties with different types of contrast or non-contrast studies being performed day to day in the radiology department and radiation protection and safety measures.
I hope you enjoyed this article and get towards your academic career and you can connect with us on all social media.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is only for educational purposes. We keep the information up to date and accurate based on different studies, you can use this article content with proper mentioning, and misuse of the content is strictly prohibited.
The article content is based on learning, experiences, and research performed by the author and we don’t provide specific guidance and recommendations at an individual level.
This article may contain external links to other websites or resources. We have no control over the concrete availability.
Don’t follow any medical advice given on this blog, without consulting with your doctor or physicians first.





